Introduction to Food Microbiology
Explore the essentials of food microbiology with this introductory category designed for beginners. From understanding the human-microbe battle to the role of lactic acid bacteria and Gram staining, these articles provide a foundation in food microbiology principles and practices. Perfect for students, newcomers, and professionals seeking a clear starting point in this fascinating field.
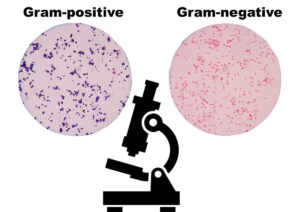
Gram Staining: Principles, Methods, and Procedures
Gram staining is a cornerstone technique in bacteriology, widely used to classify bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups based on cell wall structure. In this article, we provide a concise overview of its principles, step-by-step procedures, and interpretation of results. While this guide is aimed at beginners in food microbiology, it serves as a practical resource for understanding the fundamental aspects of Gram staining without delving into exhaustive experimental details.
Understanding the Differences between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Summary of Key Learnings
Understanding the unique characteristics and habitats of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria is essential for comprehending their role as foodborne pathogens. While Gram-positive bacteria are often associated with toxin production, Gram-negative bacteria are primarily linked to infection-type foodborne illnesses. This article provides a clear summary of their differences, exploring their physical and chemical properties, habitats, and relevance in food safety. It also addresses common misconceptions about their ecological niches and offers insights into their adaptability to various environments, including moist terrestrial settings.
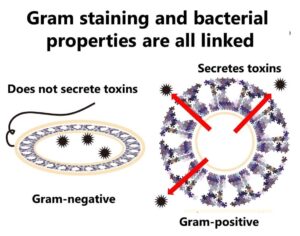
Infection-Type and Toxin-Type Foodborne Pathogens
Foodborne pathogens are a significant concern for public health, particularly in the food industry. These pathogens can be classified into two main categories: toxigenic and infectious. Understanding their differences is crucial for effective prevention and control measures. Toxigenic pathogens, often associated with Gram-positive bacteria, produce harmful toxins that cause illness when consumed. In contrast, infectious pathogens, typically Gram-negative, invade the human body and cause symptoms through direct interaction with the intestinal system. This article explores the distinctions between these two types of pathogens, their mechanisms, and their implications for food safety.
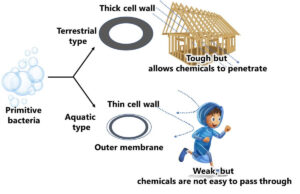
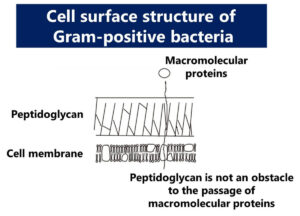
Chemical Resistance: Structural Differences Between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
The ability of bacteria to resist chemical substances is intricately tied to their cell surface structures. This page explores how the structural differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria impact their resistance to chemical agents, providing crucial insights for understanding bacterial behavior in various environments, including food safety and microbiology applications.
Structural Differences in Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria: Key Insights for Food Safety
The structural distinctions between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria are fundamental to their characteristics, habitats, and responses to environmental stressors. This article delves into these differences and their implications for food hygiene management, providing essential knowledge for professionals in food safety and microbiology.
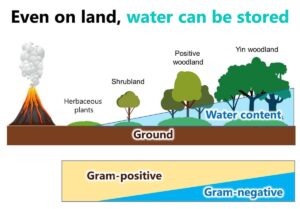
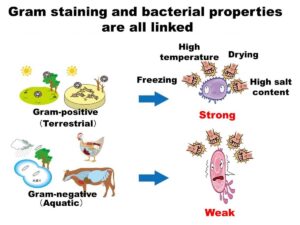
Survival Strategies of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria in Dry and Wet Environments
Bacteria have adapted to various environments over millions of years, with Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria displaying unique survival strategies in dry and wet conditions. This article explores how these differences impact their behavior in everyday environments, such as food factories and natural habitats, offering insights into their roles in microbiology and food safety.
A Comprehensive Guide to Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria: Key Differences and Environmental Adaptations
Understanding the unique characteristics of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is essential for professionals and enthusiasts in food microbiology. This page explores their structural differences, environmental preferences, and implications for food safety. Learn how these bacteria thrive in various conditions and how they influence foodborne illnesses, hygiene practices, and more.
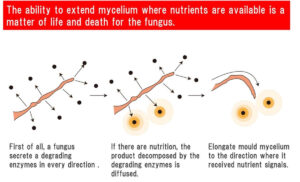
Yeast and Mold: Evolutionary Stagnation and Significance in Food Microbiology
In this article, I would like to talk to you about yeast and mold, two important microorganisms in food microbiology that are distinct from bacteria. While they are more complex than prokaryotic bacteria, both yeast and mold have reached an evolutionary dead end. Despite being heterotrophic, they have formed cell walls similar to those of plants, which hindered their development into more animal-like organisms. In this presentation, I will also discuss the positioning and significance of yeast and mold in the context of food microbiology.
Can Salmonella and E. coli O157 Spread in Toilets or Through Conversation? Understanding Foodborne Bacteria Transmission
Welcome! In this article, we delve into some essential questions about foodborne bacteria, specifically Salmonella and E. coli O157. Can these bacteria be transmitted in everyday places like toilets, or even during conversations at the dining table? While these bacteria are primarily known for causing infections through contaminated food, understanding their true transmission routes is crucial for food safety. Join us as we explore how foodborne pathogens behave and why they generally infect us only through food, shedding light on food microbiology and safe eating practices.
Gram Staining and Microbial Properties: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the fundamental differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria is critical for professionals and students in food microbiology. This page serves as a comprehensive guide to explore these differences and their practical implications in food safety, hygiene management, and microbial behavior. Below, you'll find links to detailed sections covering everything from survival characteristics to infection mechanisms and Gram staining techniques. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of microbiology!