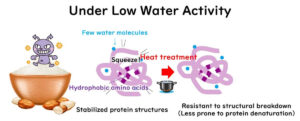
The Relationship between Water Activity in Food and Microbial Heat Resistance During Heat Sterilisation
Low water activity in food increases microbial heat resistance during heat sterilization, making careful heating of these foods crucial. How much does microbial heat resistance increase as water activity decreases? This article summarizes the impact of water activity on microbial heat resistance in foods.
Unified Protocol for Environmental Monitoring in Food Manufacturing
There are no specific protocols provided by ISO standards for environmental monitoring in food manufacturing plants. However, having concrete protocols is convenient when conducting monitoring in the field. In 2012, EU experts worked on establishing a unified protocol, particularly for the important bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. This article provides a digest of this protocol, focusing on key points with illustrations for clarity. While the focus is on Listeria, the fundamental methods of microbial sampling in food factories are also covered, making this a valuable read for beginners in food microbiology.
The Importance of Environmental Monitoring in Food Factory Hygiene Management
In the context of food factory hygiene management, the Environmental Monitoring Programme (EMP) plays a critical role as a tool for microbiological testing. Numerous cases of foodborne illness and product recalls have shown that the implementation of HACCP alone is not sufficient to prevent microbiological contamination. This article outlines the fundamental principles of environmental microbiological monitoring in food manufacturing plants.
Easy-to-Understand Food Microbiology Testing Sampling Plans in the ICMSF
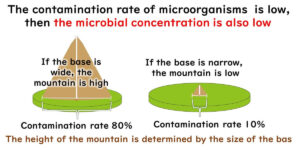
The meaning of a "negative" result in food microbiological testing varies depending on the sampling plan used. This article aims to explain the sampling plans of the International Commission on Microbiological Specifications for Foods (ICMSF) in an accessible manner. These sampling plans are adopted in the EU's food safety and process hygiene standards. Understanding the rationale behind these sampling plans is more important than memorising the plans themselves. This article focuses on explaining the "why" for beginners.
Understanding the Accuracy of Microbial Testing of Food
To ensure food safety, it's essential to grasp the purpose of microbial testing and understand its accuracy. How likely are we to correctly detect contaminated food through microbial testing? For example, what is the probability of a false negative result when testing food samples with a 10% contamination rate if we test three samples? Alternatively, how many samples need to be tested to achieve 95% accuracy in detecting contamination in food samples with a 10% contamination rate? This article will guide you through these calculations step-by-step, using Excel for ease of understanding and application.
The Role of Microbial Testing in HACCP
While HACCP aims to reduce reliance on end-product testing, microbial testing still plays a vital role in effective hygiene management. This article explains when microbial testing is still necessary, how it supports HACCP implementation, and why it should not be entirely replaced by monitoring alone—even in highly controlled environments.
Flour-based cookie dough as a route of transmission of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 infection.
Aside from food sources such as beef, the main infection routes for Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157 include contamination through livestock faeces, affecting soil in fields and environmental water, leading to tainted vegetables. However, there have been cases where seemingly unrelated foods have caused infections. An example from the US in 2009 involves a food poisoning incident from commercially packaged cookie dough made from wheat flour. This article introduces the paper by Dr. Neil and colleagues from the FDA, which summarises this incident.
How HACCP Reduces Reliance on Microbial Testing Through Process Control
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is a system designed to ensure food safety by preventing hazards before they occur, rather than relying solely on final product testing. This approach shifts the focus from microbial testing to process control, where risks are managed proactively at key points in food production.
But how does this system reduce the need for microbial testing? This article explores the fundamental concepts behind HACCP and how it has changed food safety management.
Unlocking the Potential of 16SrRNA Amplicon Sequencing in the Food Industry: Is It Truly Metagenomics?
Metagenomic analysis is a powerful tool in microbiology, allowing researchers to examine the entire genetic composition of microbial communities without the need for culturing. However, not all methods traditionally referred to as metagenomics, such as 16SrRNA amplicon sequencing, strictly fit this definition. Unlike full metagenomic approaches, 16SrRNA amplicon sequencing targets a single gene, offering a highly efficient method for microbial community analysis, particularly in the food industry.
This article explores how 16SrRNA amplicon sequencing improves food quality testing and helps resolve microbial contamination complaints. Additionally, we discuss its potential for routine microbial monitoring and zone management in food factories. Discover how this sequencing technique is shaping modern food safety practices.
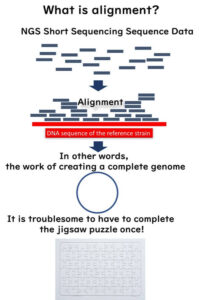
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) in Molecular Epidemiology: SNP vs. Gene-by-Gene Analysis
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) has revolutionized bacterial strain typing in molecular epidemiology. In silico MLST, SNP analysis, and gene-by-gene analysis have emerged as key methods. This article explores how WGS-based approaches, including core genome MLST (cgMLST), are replacing traditional molecular typing techniques like PFGE and MLVA in public health and food safety.