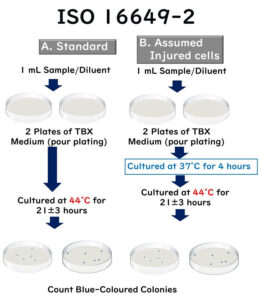
For beginners: the ISO method for E. coli testing on enzyme substrate media - explained in simple terms
Many companies are adopting the enzyme substrate medium method for their in-house testing of E. coli. But what about selecting the right medium or choosing the cultivation temperature? This article delves into the methods for testing E. coli based on the internationally recognized ISO standard, providing a detailed explanation.
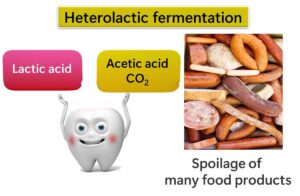
Homo- and Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria
When it comes to lactic acid bacteria, we can divide them into two main categories based on their fermentation style: homofermentative and heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria.
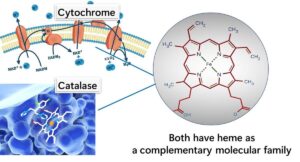
Why Don’t Lactic Acid Bacteria Have Heme? Unveiling the Unique Characteristics of Catalase-Negative Bacteria
In this article, we’ll delve into a unique question in microbiology: Why don’t lactic acid bacteria have heme, and how does this relate to their catalase-negative nature? Understanding this distinct trait sheds light on the metabolic adaptations that enable these bacteria to thrive in various environments without relying on heme-dependent enzymes like catalase.
Overflow Metabolism and the Unique Adaptations of Lactic Acid Bacteria
In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating phenomenon of overflow metabolism and how it plays a crucial role in lactic acid bacteria's survival and functionality. We’ll also define and classify lactic acid bacteria, examining their unique traits and adaptations that make them essential in food preservation and fermentation processes. By understanding why these bacteria rely on lactic acid fermentation even in oxygen-rich environments, we gain insight into their metabolic choices and the advantages they offer.
The Unique Metabolic Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of the unique metabolic traits that set lactic acid bacteria apart from other Gram-positive bacteria. In this article, we’ll uncover why lactic acid bacteria lack catalase and instead use NAD peroxidase to thrive in environments both with and without oxygen. Let’s dive into the fascinating metabolic mechanisms that make lactic acid bacteria ideal for various food fermentation processes.
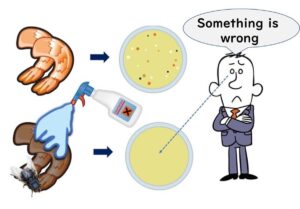
Are We Missing Something? A Closer Look at Substrate Enzyme Media as Indicators in Microbial Testing
Once upon a time, a colleague of mine shared a rather intriguing story. They had proposed to their boss to switch from testing for fecal coliforms (think E. coli, the notorious block party crasher) to using a substrate enzyme medium that utilizes β-glucuronidase activity. However, their boss shot down the idea with the objection that this medium wouldn’t cover the infamous E. coli O157:H7. So, what’s the real scoop here? Are we overlooking some vital points in our understanding?
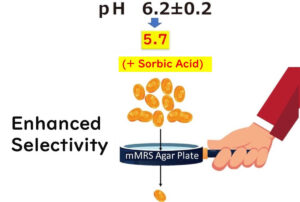
MRS Media: Tailored Nutrition for the Special Needs of Lactic Acid Bacteria
Explore the intricate relationship between the unique nutritional requirements of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and their ideal growth environment provided by MRS (de Man, Rogosa, Sharpe) media. This article highlights how MRS media, formulated with rich sources of animal proteins, vitamins, and selective growth inhibitors, caters specifically to the demanding dietary needs of LAB. By offering insights into the selective properties and nutrient composition of MRS media, we reveal its critical role in fostering the proliferation of LAB, even in the challenging conditions of laboratory research and food safety testing. In this article, let’s get to grips with just how selective media like MRS agar really are for culturing lactic acid bacteria. We'll dive into the components that make up these media.
Deciphering Culture Medium Components: A Key to Effective Bacterial Testing
In this article, we emphasize the critical importance of understanding the components within culture mediums, especially in relation to how bacteria's varying sensitivities to hydrophobic functional groups are exploited in food safety testing. We explore the strategic application of this knowledge in using desoxycholate agar and BGLB broth for testing coliforms. Dive into how mastering the intricacies of medium components not only enhances the accuracy of bacterial detection but also reflects the clever subtleties of microbiological science. Ready to unravel the secrets behind each ingredient?
Navigating International Differences in Standard Plate Count Methods for Food
When interpreting standards for standard plate count (SPC) in food, it’s crucial to understand that the method of testing and measurement can vastly influence the outcome. In fact, the definition itself might change! This article highlights the methods used to test for standard plate count in food, with a special focus on contrasting approaches between the United States (AOAC method) and the European Union (ISO method), emphasizing the broader international discrepancies. Don your lab coats and prepare for a microscopic adventure into the world of food microbiology, where every detail can lead to a world of difference!
Unveiling the Truth About Standard Plate Counting: A Crucial Tool in Food Safety Management
In this detailed article, we revisit the significance of Standard Plate Counting (SPC), a fundamental microbiological test integral to food safety practices. Often referred to as Mesophilic Count or Aerobic Plate Count, SPC measures bacteria in food samples that grow aerobically at mesophilic temperatures. However, it's crucial to acknowledge its limitations, such as not detecting certain microbial groups like anaerobes or microaerophiles. This exploration discusses the intricacies of SPC, its application under various international standards, and its role not as a definitive indicator of food poisoning risk but as a vital tool in assessing the sanitary handling and temperature management of food products.